Meadow.Foundation.Motors.Tb67h420ftg
| Tb67h420ftg | |
|---|---|
| Status |  |
| Source code | GitHub |
| Datasheet(s) | GitHub |
| NuGet package |  |
Code Example
Tb67h420ftg motorDriver;
PushButton button1;
PushButton button2;
public override Task Initialize()
{
Resolver.Log.Info("Initialize...");
button1 = new PushButton(Device.Pins.D12, ResistorMode.InternalPullDown);
button2 = new PushButton(Device.Pins.D13, ResistorMode.InternalPullDown);
button1.PressStarted += Button1_PressStarted;
button1.PressEnded += Button1_PressEnded;
button2.PressStarted += Button2_PressStarted;
button2.PressEnded += Button2_PressEnded;
motorDriver = new Tb67h420ftg(
inA1: Device.Pins.D04, inA2: Device.Pins.D03, pwmA: Device.Pins.D01,
inB1: Device.Pins.D05, inB2: Device.Pins.D06, pwmB: Device.Pins.D00,
fault1: Device.Pins.D02, fault2: Device.Pins.D07,
hbMode: Device.Pins.D09, tblkab: Device.Pins.D10);
// 6V motors with a 12V input. this clamps them to 6V
motorDriver.Motor1.MotorCalibrationMultiplier = 0.5f;
motorDriver.Motor2.MotorCalibrationMultiplier = 0.5f;
Resolver.Log.Info("Initialization complete.");
return base.Initialize();
}
private void Button1_PressStarted(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Resolver.Log.Info("Motor 1 start.");
motorDriver.Motor1.Power = 1f;
}
private void Button1_PressEnded(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Resolver.Log.Info("Motor 1 stop.");
motorDriver.Motor1.Power = 0f;
}
private void Button2_PressStarted(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Resolver.Log.Info("Motor 2 start.");
motorDriver.Motor2.Power = 0.5f;
}
private void Button2_PressEnded(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
Resolver.Log.Info("Motor 2 stop.");
motorDriver.Motor2.Power = 0f;
}
Sample project(s) available on GitHub
Wiring Example
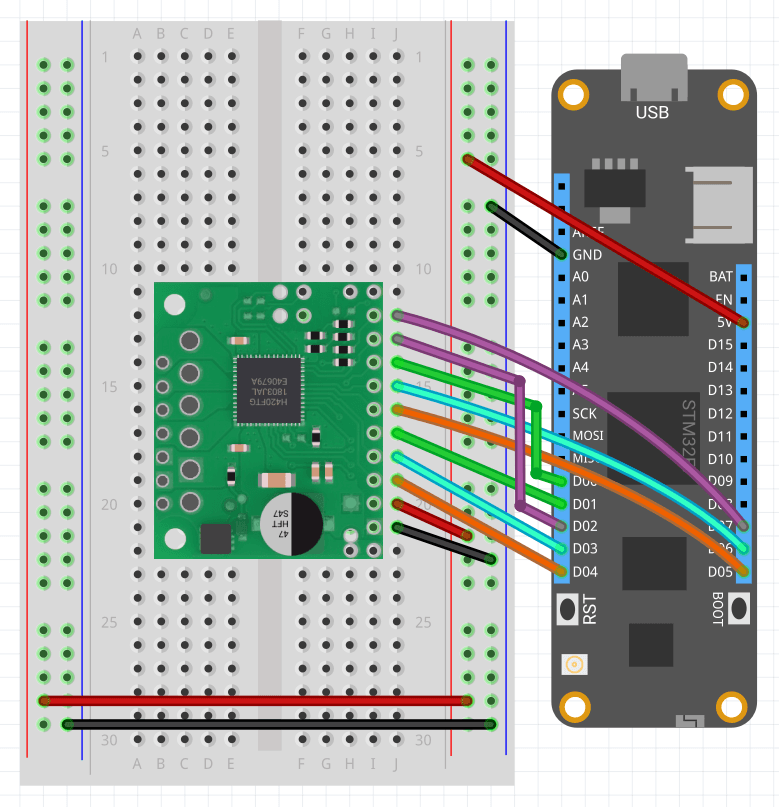
To wire a Tb67h420ftg to your Meadow board, connect the following:
| Tb67h420ftg | Meadow Pin |
|---|---|
| GND | GND |
| VCC | 5V |
| INA1 | D04 |
| INA2 | D03 |
| PWMA | D01 |
| INB1 | D05 |
| INB2 | D06 |
| PWMB | D00 |
| LOW1 | D02 |
| LOW2 | D07 |
| HBMODE | D09 |
| TBLKAB | D10 |
It should look like the following diagram: